Subtotal ₹0.00
These payments are typically made up of both principal and interest. The principal is the amount borrowed, while the interest is the cost of borrowing the money. The useful life of the patent for accounting purposes is deemed to be 5 years. So, the asset is amortized at 20% per year or 6,000 dollars per year. The accumulated amortization is the total value of the asset amortized since it was acquired. When an asset is purchased, the average useful life (period in which it will be used in business) is calculated.
Credit Cloud
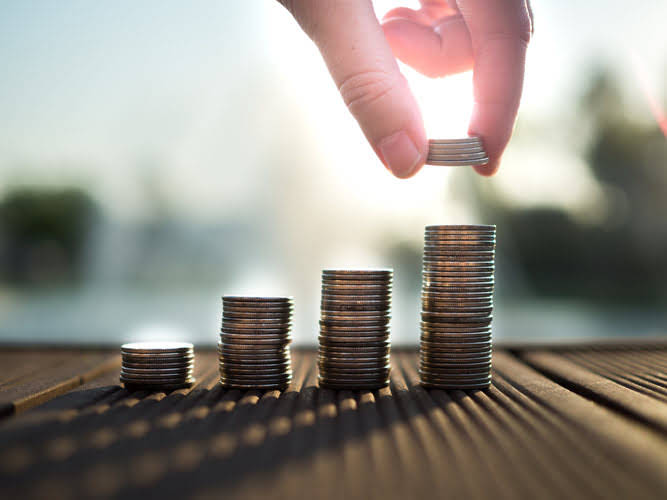

For a loan, the amortization schedule details the breakdown of each payment toward the loan principal and interest. Bureau of Economic Analysis announced a change to the way it estimates gross domestic product (GDP). Going forward, it was going to include intangible assets in its calculations of investments in the economy.
Intellectual Property

Amortization follows the matching principle in accounting, which states that expenses should be recorded in the same period as the revenues they help generate. Since intangible assets contribute to business operations over many years, amortization ensures that their costs are spread out over time. Straight-line amortization is calculated the same was as straight-line depreciation for plant assets.

What are the differences between depreciation and amortization of intangible assets?

The oil well’s setup costs can therefore be spread out over the predicted life of the well. A business might buy or build an office building and use it for many years. The original office building may be a bit rundown but it still has value. The cost of the building minus its resale value is spread out over the predicted life of the building with a portion of the cost payroll being expensed in each accounting year. Liabilities are the obligations of the company, and they can also be classified into current liabilities (due within one year) and non-current liabilities (due after one year). Equity represents the residual interest in the assets after deducting liabilities.

To do so, check this community article on how to manage an accountant user in QuickBooks Online. Accumulated amortization diminishes retained earnings and so has an impact on net income. For example, a 50 million dollar amortized value reduces the revalue of retained earnings by the same amount. Fixed Assets CS calculates an unlimited number of treatments — with access to any depreciation rules a professional might need for accurate depreciation. Companies have a lot of assets and calculating the value of those assets can get complex.
- Understanding how assets and liabilities are classified is crucial for interpreting financial statements.
- Amortization and depreciation are similar concepts, but they are used in different contexts.
- This entry reduces the value of the intangible asset on the balance sheet by 2,000 and recognizes the expense on the profit & loss account.
- It is an account in which the declining value of the asset accumulates as time passes until the asset is fully depreciated, removed from the inventory list, or sold.
- One of these concerns is how these can be calculated and recorded on financial accounts.
- However, the information gained from such accounting might not be significant because normally intangibles do not account for as many total asset dollars as do plant assets.
Let’s say a company purchases a patent for $100,000 with a Suspense Account useful life of 10 years. Assuming straight-line amortization (equal amount each year), the annual amortization expense would be $10,000. Accumulated amortization represents the total amount of an intangible asset’s cost that has been expensed as amortization since the asset was put into use. ABC Ltd. purchased the business of XYZ Ltd. for a total of 50,000, while the actual book value of the business was 30,000.
- Applying these principles keeps a company’s financial reporting clear and compliant with GAAP rules.
- This comprehensive guide on understanding the ROU asset as it relates to both finance and operating leases should help in future calculations.
- The firm files a patent for this drug and holds exclusive rights for the next ten years for 12 million dollars.
- There are, however, a few catches that companies need to keep in mind with goodwill amortization.
- Accumulated amortization is a financial term that refers to the total amount of depreciation expenses a company has taken over time for its intangible assets, such as patents or copyrights.
- Accumulated amortization is the total amount of amortization expense that has been charged against an intangible asset over time, reflecting its declining value on the balance sheet.
- Now that we have a basic understanding of the balance sheet, let’s explore how amortization fits into this financial statement and where accumulated amortization is recorded.
Importance of Amortization in Business Accounting
Amortization is necessary to accurately reflect the consumption of intangible assets over time in financial statements, ensuring transparency and compliance with accounting standards. Amortization is a vital accounting concept that reflects the gradual reduction in the is accumulated amortization an asset value of intangible assets over time. Recording amortization expense accurately is essential for maintaining financial transparency and adhering to accounting standards.

